
Excerpts from NoSpin/detroit locker® OWNER'S MANUAL

(TracTech Inc. - used without permission)
This document contains information that will be of specific interest to those who own Detroit NoSPIN differentials. It also provides considerable information that is of general interest to owners of lockers made by all manufacturers. It is provided here as a convenience.
Vehicle Performance
|
| Operation The NoSPIN differential powers both wheels…yet freely permits wheel speed differentiation when required. Prime functions
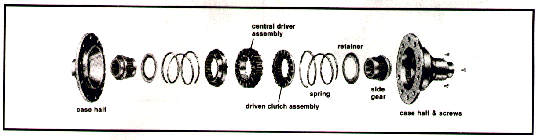
The drive axle illustrated below (Fig. 1) is equipped with a NoSPIN differential. Note that there are no spider gears, but rather two drive members, called driven clutch assemblies. They mate with a spider assembly which is driven by the ring gear through the differential support case. As long as the vehicle is operated in a straight forward or reverse direction over a smooth surface, the driven clutch assemblies remain locked to the spider assembly. The NoSPIN differential allows the whole vehicle to perform as if the axle half-shafts had been welded – the axle is completely locked. This means both wheels turn at the same speed. If one wheel loses traction or leaves the ground, the opposite wheel, which still has traction, continues to drive the vehicle until traction is regained by both wheels. There can be no one-wheel spinout (Fig. 2). When the vehicle turns a corner, or when one wheel passes over an obstruction, the outside wheel, or the wheel passing over the obstruction, must travel a greater distance and therefore faster than the other wheel. When this occurs, the NoSPIN differential automatically allows for the necessary difference in wheel speed. During a turn (Fig. 1), the inside driven clutch remains completely engaged with the spider and continues to drive the vehicle. The outside driven clutch automatically disengages from the spider, allowing the outer wheel to turn freely in the turn. When the vehicle completes the turn, the outside driven clutch automatically reengages the spider, as both wheels again travel at the same speed. |
| Troubleshooting An important function of an owner/operator in the field is that one of the many hats he is required to wear is the one labeled "trouble shooter". Troubleshooting can be a very frustrating, elusive job. However, if some basic rules are followed in a systematic order, solutions can be easily obtained. The following guidelines can be utilized for trouble shooting both on and off the highway vehicle applications. However, some techniques used for on-highway vehicles are not as important for off-highway vehicles:
The following chart will assist owners and operators of NoSPIN differential equipped vehicles to diagnose and correct problems related to vehicle performance. Potential problems are stated on the left; possible causes for those problems are listed, by number, on the right. The explanation of these "problem causes" follows. |
Trouble Shooting Section
| Problem | Possible Cause(s) |
||||||||||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | |
| Hub studs shearing; rear tire scuffing; axle shaft breakage | · | · | · | · | · | · | |||||||||
| Steering difficulty; vehicle pulls on straight forward driving or tends to go straight when making turns | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | ||||||
| No differential action; binding in turns | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | ||||||||
| Excessive driveline noise* | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | |||||||
| Excessive tire wear | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | ||||||
| Grinding noises | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | ||||||||
| Continuous "clicking" sound in straight forward driving | · | · | · | · | |||||||||||
| Excessive backlash in vehicle drivetrain; engine lug or vehicle surge during turns | · | · | · | · | |||||||||||
| Tendency to side-slip or "fishtail" on icy roads | · | ||||||||||||||
| Sluggish reengagement of NoSPIN differential clutch assemblies | · | · | |||||||||||||
| Difficulty in turning vehicle from standing start | · | · | · | · | · | ||||||||||
| Erratic operation of NoSPIN differential; premature wear or failure of NoSPIN differential components | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | · | |||||
| NOTE: NoSPIN differentials
will emit occasional "metallic" sounds due to backlash built into the unit. This
is normal! See backlash under Vehicle Performance in the NoSPIN Owners Manual.
TROUBLE SHOOTING – Cont’d Possible Causes for Vehicular Problems
|
| Glossary Articulated – Refers to vehicles that are joined in the middle and turn around this joint, as in "articulated farm tractor". Axle Carrier – The differential and ring and pinion gears are mounted on the axle carrier; the "center section" of the axle housing. Axle Gear Ratio – The ration between the number of teeth on the ring gear and the number of teeth on the pinion gear (e.g. 3.92:1.00) Axle Housing - The support member of the axle which sustains the weight of the vehicle and houses the axle carrier assembly. Backlash – The designed clearance between mating components in the driveline (e.g., gear sets, spine couplings, etc.) Case Assembly – The differential housing (usually consisting of the two case halves; contains the differential assembly) Case Bearing (Carrier Bearing) – the bearings that mount to the hubs on the differential support case. Case Pilot Bore – the locating diameter in the differential case from which the differential side gear is installed. Center Cam – The control element of the NoSPIN differential. The center cam is used to lift the drive members from engagement by means of cam ramps. Central Driver – An outer splined member (similar to the spider) having torque carrying teeth on both sides; the "center piece" of the NoSPIN differential. Clutch Pack Differential – A limited-slip differential which uses friction plates and/or springs to partially reduce wheel spin. Detroit Locker Differential – Trademark given to "light duty" NoSPIN differentials (NoSPIN and Detroit Locker are operationally identical.) Manufactured by Tractech. Differential – Axle gear assembly which allows one axle shaft and wheel to turn slower or faster than the other when negotiating a turn. Differentiation – The different rate of speed between two wheels of an axle when making a turn or over uneven surfaces. Driveline – Components used to propel the vehicle driveshaft and universal joints, transmitting torque from transmission to drive axle (same as drivetrain). Driven Clutch – Member that is used to provide torque to another member, such as to the side gear. Each NoSPIN differential has two driven clutches. Drivetrain – A series of components which transmit power from the engine to the wheels/tires (i.e., transmission, propeller shafts, transfer case, axle, differential, shafts, etc). Double Reduction – Dual gear reduction used in rear axles. Fishtailing – Side slipping of the vehicle caused by traction instability. G.C.W. – Gross Combination Weight. G.V.W. plus vehicle weight and payload of towed vehicle. G.V.W. – Gross Vehicle Weight. Total weight of vehicle and payload. Gear Support Case - Case used to support the differential. Same as case assembly. Ground Coefficient – The horizontal force required to move a body, divided by the weight of the body. The amount of friction at the ground; the "quality" of the ground surface (e.g., ice, snow, dirt, etc.) Helical – "Angled" gear tooth form. Holdout Ring – Ring which assembles to NoSPIN differential clutch; maintains clutch disengagement in a turning mode. Indexing – A passing of one member over another, causing a slight audible sound from their contact (usually associated with the NoSPIN differential). Input Torque – Measurement of available power. Lead Ratio – On unequal wheeled four wheel drive tractors the transmission is so geared that any difference in road speed of the two axles results in a faster speed for the front wheels (lead or overrun), this prevents the front wheels from being pushed. Limited-Slip Differential – A differential which utilizes some means of partially reducing, but not totally eliminating, individual wheel spin (e.g. clutches, springs, biasing pinion gears, etc.). Locking Differential – A differential that provides a locked axle condition. Can be manual or automatic, as in hydraulic locking differential or NoSPIN differential. Machined Splines – Splines that have been manufacturer by shaping, hobbing, broaching, or slotting. NoSPIN Differential – Trademark of automatic, positive locking differential. Manufactured by Tractech. Overrun Ratio - On unequal wheeled four wheel drive tractors the transmission is so geared that any difference in road speed of the two axles results in a faster speed for the front wheels (lead or overrun), this prevents the front wheels from being pushed. Parallel Splines – Series of parallel keys cut along the axle shaft which mate with corresponding slots in the differential side gear. Payload – Actual weight of useful cargo carried by vehicle. Pinion (Input) Gear – The gear that is directly connected to the driveshaft which propels the differential and ring gear and provides power to the axle. Planetary Axle – Axle having a gearset arrangement in a concentric pattern; consisting of a sun gear surrounded by pinion gears which mesh with an annulus ring gear. This gearset provides torque multiplication in a reduced area on the same center line as the axle shaft usually located on the hub ends of axle. Pre-Load – Differential bearing adjustment achieved by adding or subtracting shims. R.P.M. – Revolutions Per Minute. Term used to define rotation. Ring Gear – The gear that is attached to the differential case and driven by the pinion gear. Rolled Splines – Splines that are manufactured by the use of rolling dies to form the spline configuration. Shims – "Spacer" used to achieve differential bearing adjustment. Side Gear – The gear that is mounted in the differential case; has the axle shaft splined to it; driven by the pinion gear. Single Speed – Axle or transfer case having a single gear ratio. Shockload - A force caused by sudden impact. Spider – The "center piece" of a standard, clutch-pack or NoSPIN differential; having a spider-like shape. Spider Cross – Two or four armed member used to mount the standard differential pinion gears. Spider Gear(s) – Bevel pinion gears that are mounted on spider cross that drive the side gears of standard or clutch type differentials. Splines – "Teeth" on axles that mate with "teeth" (splines) on differential side gear. Snap Ring – A circular expandable ring that is used to retain two members together, as a snap ring in a NoSPIN differential that retains the spider and center cam. Standard Differential – Open or conventional differential with no means of traction control. Tag Axle (Tandem) – Non-powered rear axle which follows drive axle. Provides additional load-carrying capacity and distribution. Tapered Splines – Cone shaped spline configuration. Thrust Blocks – Support mechanism used to prevent ring and pinion gear deflection. Thrust Washer – Used in conventional differential to reduce wear to the support case. Torque – Force having a twisting or turning effect. Also used in conjunction with the term "power". Trunnion – Journals allowing pivoting or turning, such as on a spider cross. On a NoSPIN differential, the arm (there are four) which supports the differential in the case assembly. Two-speed – Axle or transfer case having two selective gear ratios. Understeer – The condition of steering when making a turn that causes the vehicle to go straight rather than turn freely. Wheelbase – Distance between center lines of front and rear axles or to the center line of tandem axles. |
Disclaimer:
This information is provided as a reference and is not meant to be a definitive source of information about lockers made by any manufacturer. Use of this information is at your own risk. This information may become obsolete over time. No guarantee is made that it will be updated to reflect changes in products described.
In other words, if you are going to make decisions about the care, use, installation, maintenance, purchase or diagnosis of locker problems, do not rely on this document - refer to the current, relevant documents produced by the manufacturer of your locker or differential device.
Return to Detroit Locker Page
Photos, Layout and Design © 2001,2002 Paul M. Provencher All Rights Reserved.
Contents of this Web Site may not be used without written permission
Text and images on this page © TracTech, Inc.
Visitors since 10/26/02